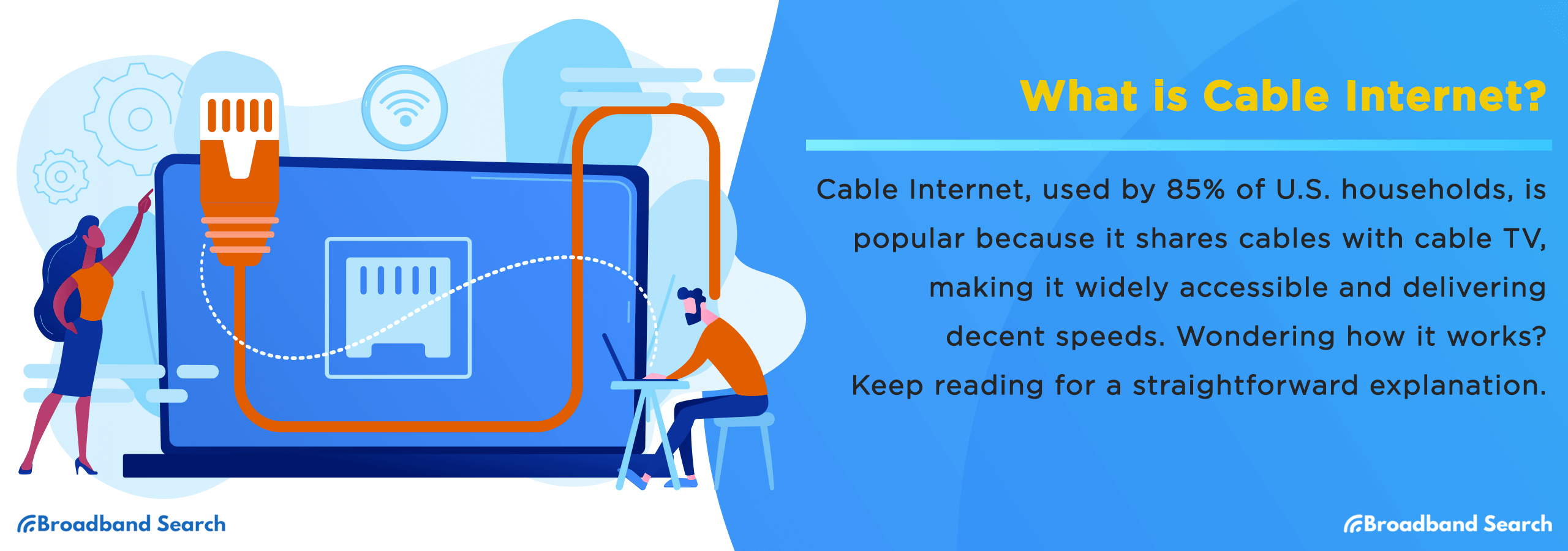
Cable internet is a high-speed broadband connection that delivers internet access through the same coaxial cables used for cable television. It’s one of the most widely available broadband types in the U.S., reaching about 85% of households (FCC, 2025).
Cable internet provides fast, reliable connections without the need for satellite dishes or special line installations. It’s an “always-on” connection that’s ideal for streaming, gaming, remote work, and more.
Key Takeaways
- Cable internet delivers broadband through the same coaxial lines used for cable TV.
- DOCSIS 3.1 and 4.0 enable gigabit speeds and low latency.
- It’s available to 85% of U.S. households — more than fiber.
- Average cost: $40–$100/month.
- Best for: families, streamers, and small businesses needing reliable connectivity.
- Alternatives: fiber (faster but less available), DSL (slower), satellite (rural access).
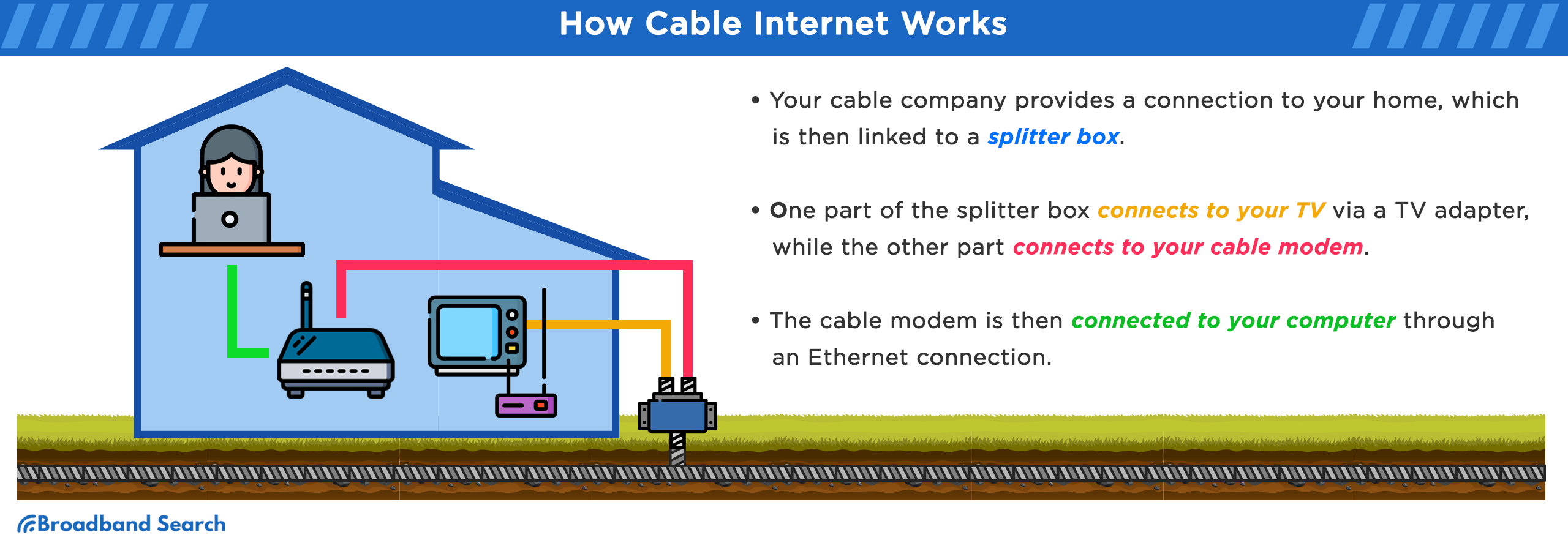
How Does Cable Internet Work?
Cable internet uses coaxial cables to transmit data signals between your internet service provider (ISP) and your home modem. Here’s the basic process:
- Signal Transmission: Digital data is encoded and sent through copper-based coaxial cables.
- Reception: Your modem decodes these signals and translates them into data your devices can use.
- ISP Connection: Your ISP manages your connection and authenticates access to the web.
Unlike dial-up or DSL, cable internet stays connected 24/7 and shares bandwidth within a neighborhood network, meaning performance can fluctuate during peak times.
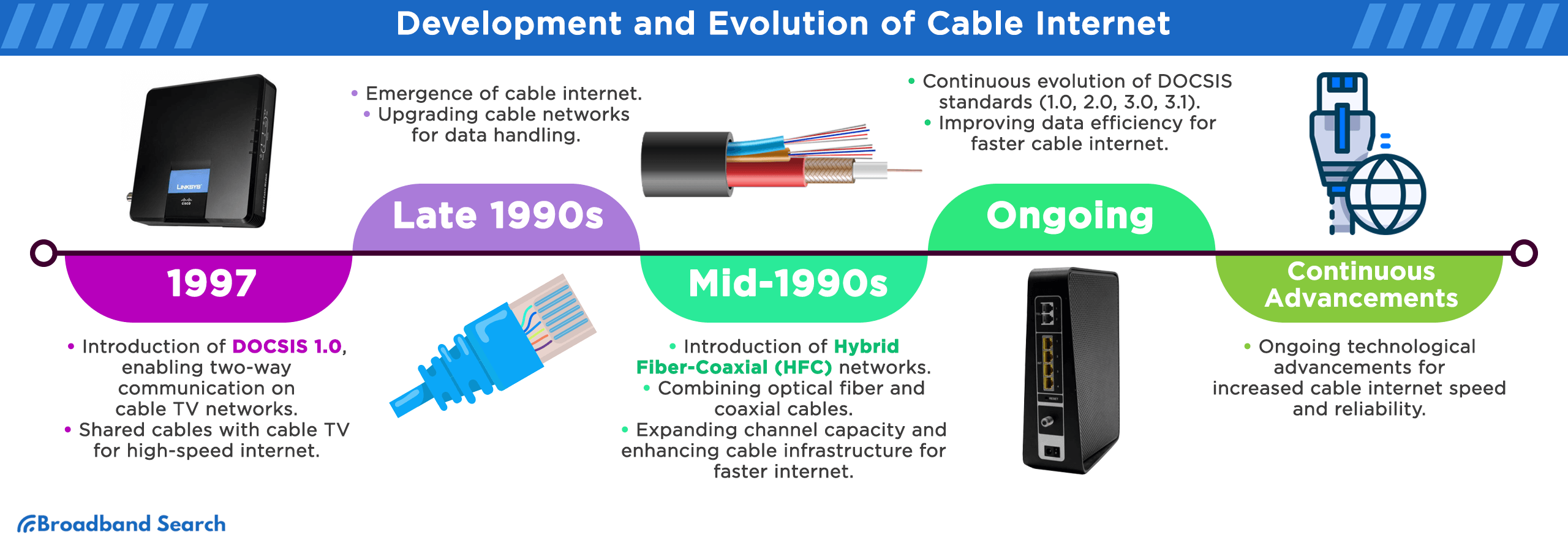
What Is DOCSIS and Why Does It Matter?
DOCSIS (Data Over Cable Service Interface Specification) is the standard that allows internet data to travel over TV cables.
| DOCSIS Version | Year | Max Download Speed | Max Upload Speed | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.0 | 1997 | 40 Mbps | 10 Mbps | First two-way data transfer |
| 2.0 | 2002 | 40 Mbps | 27 Mbps | Improved uploads, less lag |
| 3.0 | 2006 | 1 Gbps | 200 Mbps | Channel bonding introduced |
| 3.1 | 2013 | 10 Gbps | 1 Gbps | Faster speeds, better efficiency |
| 4.0 | 2019 | 6 Gbps | 6 Gbps | Full duplex (simultaneous up/down) |
Modern ISPs typically use DOCSIS 3.1 or 4.0, offering gigabit speeds and lower latency.
What Hardware Does Cable Internet Require?
Cable Modem
The modem bridges your devices to the ISP’s network. A DOCSIS 3.1 modem is ideal for gigabit service or households with high data usage.
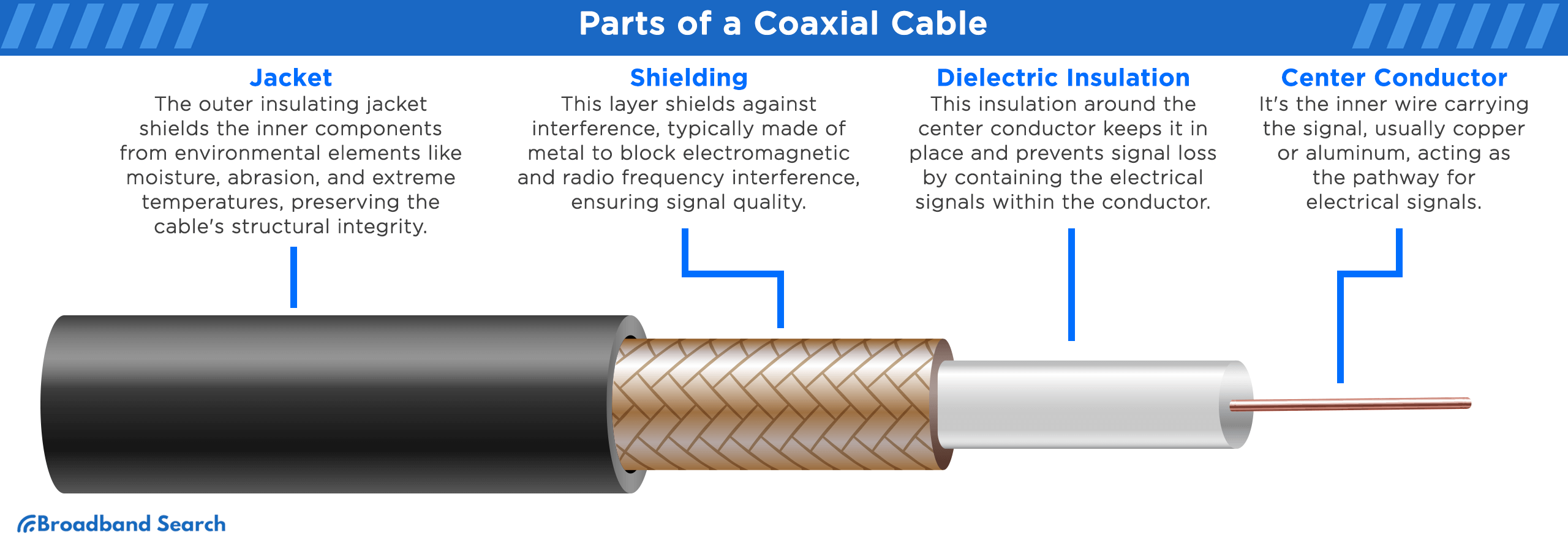
Coaxial Cables
Modern coaxial cables (like RG-6) are built with stronger shielding and larger diameters for better performance and fewer signal losses.
CMTS (Cable Modem Termination System)
Located at your ISP’s data center, the CMTS manages data traffic between multiple homes and the wider internet—think of it as the “air traffic controller” for your connection.
How Fast Is Cable Internet?
Typical cable internet speeds (as of 2025):
| Plan Tier | Download Speed | Upload Speed | Latency |
|---|---|---|---|
| Entry-Level | 50–100 Mbps | 5–10 Mbps | ~30–50 ms |
| Mid-Tier | 300–600 Mbps | 10–30 Mbps | ~25–40 ms |
| Gigabit | 940–1,200 Mbps | 35–50 Mbps | ~15–30 ms |
Speeds may vary based on your hardware, ISP, and the number of users online at once.
How Does Cable Internet Compare to Other Connection Types?
| Internet Type | Top Speed | Latency | Availability | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cable | Up to 1 Gbps | 20–40 ms | ~85% of U.S. homes | Widely available, reliable, affordable | Shared bandwidth, slower uploads |
| Fiber | Up to 10 Gbps | 1–10 ms | ~45% | Symmetrical speeds, ultra-fast | Limited availability, higher cost |
| DSL | Up to 100 Mbps | 40–70 ms | ~88% | Uses phone lines, low cost | Slower speeds |
| Satellite | Up to 300 Mbps | 600+ ms | ~99% | Rural access | High latency, expensive |
How Much Does Cable Internet Cost?
Cable internet pricing varies by provider and region:
| Provider | Starting Price | Typical Speed Range | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Xfinity | $40–$80/mo | 75–1200 Mbps | Available nationwide |
| Spectrum | $50–$90/mo | 300–1000 Mbps | No data caps |
| Cox | $40–$100/mo | 100–1000 Mbps | Includes modem rental |
| Optimum | $45–$80/mo | 300–1000 Mbps | Bundle discounts available |
| EarthLink | $60–$100/mo | 100–1000 Mbps | Partner network access |
Source: FCC and provider websites (2024 data)
What Are the Pros and Cons of Cable Internet?
Advantages
- High Speeds: Up to 1 Gbps download speeds for smooth streaming, gaming, and video calls.
- Reliable Performance: Consistent connections for most households and businesses.
- Bundling Options: Combine internet, TV, and phone services under one bill.
Disadvantages
- Shared Bandwidth: Slower speeds during peak hours.
- Possible Data Caps: Some ISPs limit monthly usage.
- Installation Needs: May require a technician for setup or repairs.
Is Cable Internet Still Worth It in 2025?
Yes. Cable internet remains one of the most accessible and cost-effective broadband options for U.S. households. With DOCSIS 4.0 expanding gigabit availability, it continues to offer strong performance for streaming, work, and entertainment.
While fiber delivers faster upload speeds, cable is still the most practical high-speed option for areas without fiber infrastructure.
FAQ
What is cable internet, and how does it work?
Cable Internet is a high-speed internet service that utilizes the existing cable TV infrastructure to deliver internet access to homes and businesses. It works by transmitting data signals over coaxial cables, providing fast download and upload speeds.
What are the advantages of cable internet?
Cable Internet offers high-speed access, reliability, and the ability to bundle services like TV and phone. It's ideal for bandwidth-intensive tasks like streaming, gaming, and remote work.
What is DOCSIS, and how does it impact cable internet?
DOCSIS (Data Over Cable Service Interface Specification) is a set of standards that govern how data is transmitted over cable networks. Different versions of DOCSIS have led to improvements in speed and performance for Cable Internet.
How can I optimize my cable internet connection at home?
To optimize your cable internet, ensure your modem and router are up to date, use a wired connection when possible, and regularly restart your equipment. Additionally, consider upgrading your plan if you have multiple devices or heavy internet usage.
How can I switch to cable internet from my current provider?
To switch to cable internet, contact a local cable internet provider, choose a suitable plan, and schedule the installation. The provider will guide you through the process, including any necessary equipment upgrades.