Don’t let optical network terminal (ONT) problems disrupt your fiber-optic experience. At BroadbandSearch, we developed this guide to help you avoid unnecessary service calls and prevent frustrating downtime. We’ll walk you through common ONT issues, practical DIY fixes, and tips for long-term maintenance, so you can troubleshoot effectively and know when it’s time to call in professional support.
What Is an ONT?
An ONT converts the fiber-optic light signals from your internet provider into electrical signals your home network can use. Think of it as the bridge between the high-speed fiber line outside and your router.
Key components:
- Optical port: Where the fiber-optic cable connects.
- Power supply: AC adapter or battery backup.
Common ONT Problems and What They Mean
Its performance is crucial for a stable, high-speed connection. Here are the most frequent issues you might encounter with your ONT.
1. Power-Related Issues
A dead or faulty ONT often points to a power problem.
Symptoms:
- The ONT won’t power on at all.
- Lights are flickering or behaving abnormally.
- You notice a burning smell or the unit feels excessively hot.
- Ethernet ports: Distribute the internet connection to your router and local area network (LAN).
- Real-life example: If your internet suddenly drops but your router seems fine, the ONT could be the culprit.
Common Causes:
- Local power outages. See how power outages affect fiber networks for details.
- A faulty power adapter or a blown fuse.
- Loose or damaged wiring.
- An aging power supply unit (most have a typical lifespan of over 5 years). According to ONTOLT, average lifespan of ONUs (similar to ONTs) is 5-10 years.
2. Connectivity Problems
Even with power, the signal itself can be disrupted.
Loss of Signal May Come From:
- Fiber cuts: Often happens during nearby construction.
- Damaged cables: Physical damage from bending, chewing by animals, or household accidents. A FiberLight report states ~28% of fiber outages are caused by animals chewing cables.
- Dirty or loose connectors: Dust and insecure connections are common culprits.
- Internal ONT hardware failure.
Fluctuating Signal Strength Often Relates To:
- Weather interference: Accumulating ice or snow can temporarily disrupt network infrastructure. See how fiber performs during storms at C Spire’s blog: How fiber internet stays reliable in bad weather conditions.
- Loose cables: Wind can affect improperly secured outdoor cables.
- Electronic interference: Placing the ONT too close to other electronics.
- Signal attenuation: The signal naturally weakens over very long distances; see studies on fiber signal loss in long-haul fiber (e.g. via IEEE papers on attenuation).
3. Hardware Damage
Physical damage is a straightforward but serious issue.
- Physical damage: Obvious cracks, dents, or water exposure can break the internal connections and disrupt the signal flow.
- Wear and tear: Most ONTs last about 5-10 years before internal components start to degrade, leading to random disconnections or slower speeds
4. Firmware and Software Issues
The ONT’s internal software can cause problems if it’s not managed properly.
- Outdated firmware: Can lead to slower speeds, security vulnerabilities, and general instability.
- Software conflicts: May cause confusing error messages, inconsistent speeds, and random disconnects.
How Do I Troubleshoot ONT Issues?
Before calling for help, try these simple steps.
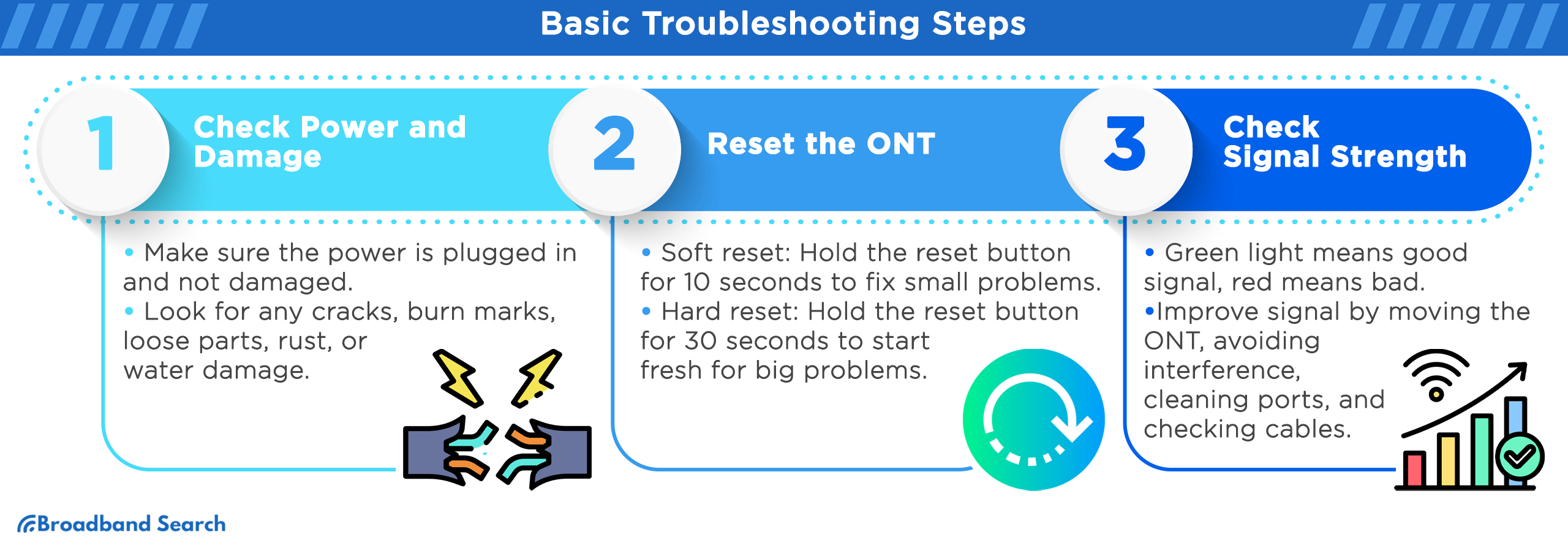
Step 1: Check the Power
- Ensure the power adapter is securely plugged into both the ONT and a working wall outlet.
- Test the outlet by plugging in another device, like a lamp.
- If possible, try a different compatible power adapter.
Step 2: Inspect for Physical Damage
- Look for visible cracks, burn marks, or signs of water exposure.
- Gently check if any parts feel loose or rattle.
Step 3: Reset the ONT
- Soft Reset: Press and hold the reset button for 10 seconds. This reboots the device and can fix minor glitches without erasing your settings.
- Hard Reset (Factory Reset): Press and hold the reset button for 30 seconds. This is a last resort, as it restores the ONT to its factory settings. Contact your internet provider before doing a hard reset.
Step 4: Interpret the Signal Lights
The lights on your ONT are diagnostic indicators. While models vary, they generally follow this pattern:
- Green: Strong, stable signal.
- Amber (or Orange): Moderate signal; connection is okay but not optimal.
- Red: Poor or no signal. This indicates a significant problem.
- Flashing: Active data transfer or a potential error. Refer to your ISP’s guide for specifics.
Signal Lights Chart
| Light Color | Status | What It Means | What to Do |
|---|---|---|---|
| Green | Solid | Strong, stable signal | Normal operation - no action needed |
| Amber/Orange | Solid | Moderate signal; connection is okay but not optimal | Monitor performance; contact ISP if speeds are slow |
| Red | Solid | Poor or no signal - significant problem | Check connections, restart ONT, or contact ISP |
| Any Color | Flashing | Active data transfer or potential error | Normal during data transfer; if persistent, check ISP guidelines |
| No Light | Off | No power or complete failure | Check power connections and adapter |
Advanced ONT Troubleshooting
If the basics don’t work, these next steps can help isolate the problem.
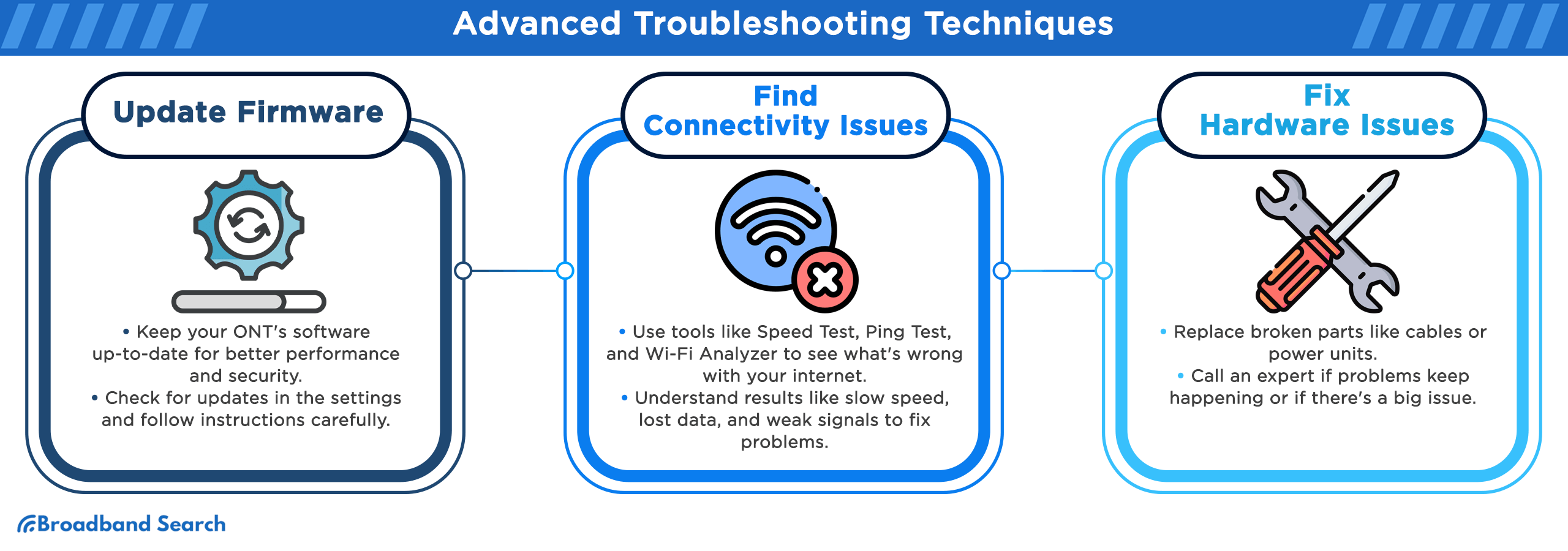
Update the Firmware
- Check your device manual or manufacturer’s website for detailed firmware instructions.
- Log into your ONT’s admin interface through a connected device.
- Find the firmware or update section and check the current version.
- Compare it to the latest version available on the manufacturer’s or your ISP’s website.
- Before updating, back up your current settings.
- Follow the instructions carefully and restart the ONT after the update is complete.
Use Network Diagnostic Tools
These tools help identify specific connectivity issues and provide measurable data to understand your connection's performance:
- Speed Test: Measures your current download and upload speeds (e.g., testmyspeed.com). Compare results to your plan's promised speeds—significant differences indicate potential ONT or line issues.
- Ping Test: Checks for latency (delay) and packet loss (data getting lost in transit). High ping times (over 100ms) or packet loss above 1% suggests network problems.
- Traceroute: Shows the path your data takes to a destination, helping identify where slowdowns or "bottlenecks" occur. If delays happen at the first hop, the issue is likely with your ONT or local connection.
Replace Faulty Components
Some parts are easy to replace yourself, like Ethernet cables or even the power supply unit. However, if you suspect issues with optical modules or see burnt circuit boards or damaged ports, it’s best to call a professional.
How Do I Keep My ONT Working Optimally?
A little maintenance goes a long way in preventing future headaches.
Routine Maintenance
- Gently dust the unit with a soft, dry cloth and ensure the ventilation ports are clear.
- Periodically check that all cables are securely connected.
Environmental Best Practices
- Keep the ONT in a cool, dry, and well-ventilated area.
- Avoid direct sunlight, heat sources, and moisture. Its ideal operating temperature is typically between 32°F and 104°F (0°C and 40°C).
- Secure loose cables to prevent them from being accidentally pulled or damaged.
Stay Updated
- Schedule regular checks for firmware updates.
- Consider subscribing to manufacturer or ISP notifications for automatic alerts.
- Always download updates from trusted, official sources.
- Restart your Wi-Fi router regularly to offload caches
When to Call in the Pros
Sometimes, a DIY fix isn’t enough. Contact your internet service provider (ISP) if you experience:
- Persistent signal loss, even after resetting the ONT.
- Severe physical or water damage.
- Recurring power failures that aren’t related to your home’s electricity.
- Complex software errors or a firmware update that fails.
Pro Tip: Before you call your ISP, write down the troubleshooting steps you’ve already taken. This information can help the support technician diagnose the problem much faster.
Keep Your Fiber Flowing: Key Takeaways
- The ONT is essential for your fiber internet. If it fails, your connection fails.
- Most issues are related to power, connectivity, or software and can often be fixed with simple troubleshooting.
- Preventive maintenance extends your ONT's lifespan (which is typically 5-10 years). This includes keeping it clean, ensuring cables are secure, and performing regular firmware updates
- Know when to ask for help. For severe hardware damage or recurring complex issues, professional support is your best bet.
By staying proactive, you can save time, money, and frustration while keeping your fiber connection fast and reliable.
FAQ
What is an optical network terminal?
An optical network terminal (ONT) is a device that converts fiber-optic light signals from your internet service provider into electrical signals that your home network equipment can use. It serves as the critical connection point between the fiber-optic cable and your router.
What equipment is needed for fiber internet?
For fiber internet, you typically need an ONT (provided by your ISP), a router to distribute the internet connection throughout your home, and Ethernet cables to connect devices. Some setups may also include a modem, though many fiber connections connect the ONT directly to the router.
How long do ONTs typically last?
Most ONTs have a lifespan of 5-10 years under normal operating conditions. Factors like environmental conditions, power fluctuations, and usage patterns can affect this timeframe. Regular maintenance can help extend the device's life.
Can I replace my ONT myself?
Generally, ONT replacement should be handled by your internet service provider or a certified technician. The device requires specific configuration and may need professional installation to ensure proper connection to the fiber network.
What's the difference between an ONT and a modem?
An ONT is specifically designed for fiber-optic networks and converts light signals to electrical signals. A traditional modem is used for cable or DSL connections and modulates/demodulates signals over copper lines. In fiber setups, the ONT essentially replaces the traditional modem.