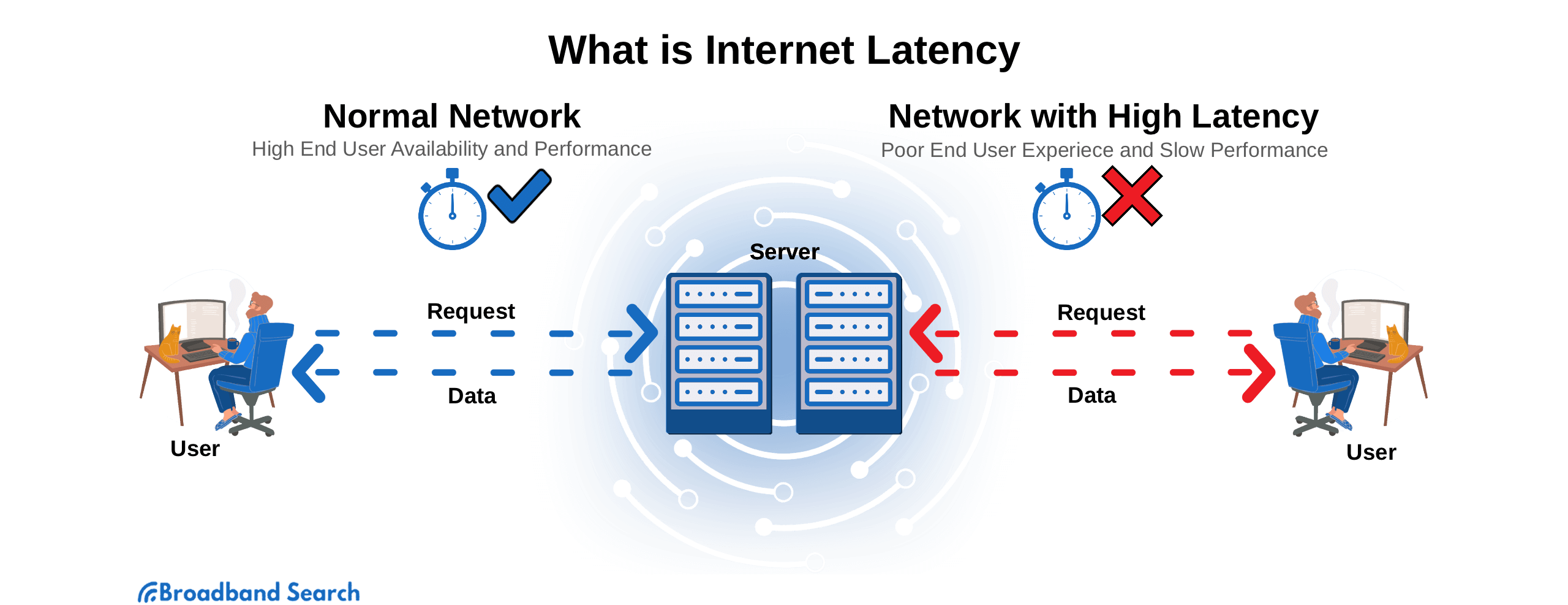
Internet latency is the delay between when you click something online and when it actually happens. If it takes too long for your device to “talk” to the internet and get a reply, you’ve got high latency—also known as lag.
Quick Answer: High latency makes websites slow, video calls choppy, and games laggy. You can reduce it by restarting your router, checking your devices, and scanning for viruses.
What Are the Signs of High Latency?
Below are the top signs that internet latency is impacting your online experience.
- Slow website loading – Pages take longer than usual to open, even with fast internet.
- Buffering or stuttering videos – Shows freeze or stop and start while you’re watching.
- Choppy voice or video calls – People cut out or move like a slideshow.
- Dropped connections – Apps or games kick you out randomly.
What Is Jitter (And Why It Makes Lag Worse)?
Jitter happens when your internet signal is shaky instead of smooth. Think of jitter like a bumpy road for your data—it makes real-time stuff like calls and games harder to use.
- Fiber: Avg. Jitter is 1–5 ms - It feels super smooth
- Cable: Avg. Jitter is 5–30 ms - It feels mostly good, but can lag at busy times
- DSL: Avg. Jitter is 20–50 ms - It often feels jumpy
- Satellite: Avg. Jitter is 50–100+ ms - It feels very slow at times—bad for live calls/games
Key Point: Low jitter = steady connection. High jitter = glitchy experience.
What Causes High Latency?
Common internet latency causes include distance, congestion, and equipment issues.
High internet latency doesn’t just happen randomly. There are several reasons why your connection might feel slow or unresponsive—even if your download speeds seem fine.
Quick Answer: High latency is usually caused by distance to a server, network congestion, bad equipment, or using an internet type that naturally has more lag (like satellite).
1. You’re Too Far from the Server
The farther your data has to travel, the longer it takes to get there and back. That means if you're in New York but using a server in Australia, your latency will go up—even with a fast connection.
Try this: Connect to a server that’s closer to your location when possible.
2. Too Many Devices Are Online at Once
If a lot of people in your house—or neighborhood—are online at the same time, the network can get crowded. This is called network congestion, and it can slow down how fast your data gets through.
Look out for: Slower speeds during peak hours (like after school or in the evening).
3. You’re Using Outdated or Glitchy Equipment
Old or broken routers and modems can make latency worse. Even your computer or phone might be part of the problem.
Try this first:
- Restart your modem and router.
- Replace any devices that are more than 5 years old.
- Use wired connections (Ethernet) if possible.
4. Wireless Interference Is Getting in the Way
Wi-Fi signals can get blocked or slowed down by walls, other electronics, or even your microwave. That interference can cause lag and spikes in latency.
Quick fix: Move your router to a central location or switch to a wired connection for key devices. Latency when connected via Ethernet cable can come in at about 2-3ms, providing a steady connection. Latency on a wireless connection can be as high as 20ms locally, according to DPC Technology.
5. Your Type of Internet Is Slower by Nature
Some types of internet service just come with higher latency. Here's how different types stack up:
- Fiber: Typical latency is between 5–15 ms and is rated ✅ Very Low
- Cable: Typical latency is between 15–40 ms and is rated ⚠️ Low to Medium
- DSL: Typical latency is between 30–70 ms and is rated ⚠️ Medium
- Satellite: Typical latency is between 500–700+ ms and is rated ❌ Very High
According to internal data, fiber users report the lowest latency and most reliable connections—especially for gaming and video calls.
Pro Tip: Run a Virus Scan
Malware or hidden programs can use up your internet in the background, causing lag and high latency. Before you change your setup, scan your computer or device for viruses or unknown programs. Most computers have built-in tools for this—run them regularly to stay safe and fast. This small step can fix big problems quickly.
How Is Latency Measured and Why It Matters
Latency is measured in milliseconds (ms), with a millisecond being one-thousandth of a second. While this unit seems incredibly small, even slight variations in latency can greatly affect how smoothly your internet performs.
Here’s an example breakdown to help visualize:
- 20 ms latency: Ultra-fast, ideal for gaming or real-time communication.
- 100 ms latency: Acceptable, but slight delays might be noticeable for certain activities.
- 500 ms latency: Frustratingly slow, causing severe lags for gaming, video calls, and even basic browsing.
Latency is usually measured during a speed test under the metric called "ping." A lower ping corresponds to quicker responses from your internet, which gives you a smoother online experience.
Ideal Latency for Daily Online Activities
Different activities require varying levels of latency for optimal performance:
- Web browsing: Works well with latency under 100 ms.
- HD video streaming: Seamless playback with latency below 100 ms.
- Video calls (Zoom, Teams, etc.): Clear audio and visuals under 75 ms.
- Online gaming: Smooth, fast-paced action with latency below 50 ms.
Pro Tip: If your ping exceeds 150 ms, you’ll likely notice slower responses or lags in almost all online activities.
How Can You Reduce High Latency?
If your internet feels laggy or delayed, there are several simple things you can try to improve latency. While not every fix works for every setup, many of these tips can make a big difference—fast.
Quick Answer: To reduce latency, restart your router, close background apps, use a wired connection, scan for viruses, and choose a better internet plan if needed.
1. Restart Your Router and Modem
This is the easiest fix—and it works more often than you’d think.
Here’s how to do it:
- Unplug your router and modem from the power outlet.
- Wait 30 seconds.
- Plug them back in and wait 1–2 minutes for them to restart.
Why it works: This clears out any errors or overloads that build up in your devices' memory, which can cause lag.
2. Close Apps Running in the Background
Some programs keep using your internet even when you're not using them, which can eat up your bandwidth. Streaming services, file downloads, cloud backups, and even updates can all cause latency.
Try this:
- Close apps or tabs you're not using.
- Pause any large downloads or updates until you're done gaming, calling, or working.
3. Clear Your Cache and Cookies
While this doesn’t directly change latency, clearing your cache and cookies can make your device and browser run faster.
Steps:
- Go to your browser history settings.
- Choose "Clear cache" and "Clear cookies."
- Restart your browser.
Pro tip: This can also help websites load more smoothly and prevent small errors.
4. Use a Wired Connection (If You Can)
Wi-Fi is convenient, but it’s not always the fastest. Using an Ethernet cable gives you a direct connection and usually lower latency.
Many gamers and streamers prefer wired connections for more stable performance—especially in fast-paced online games.
5. Switch Servers or Locations
If you're playing a game or using an app with high lag, try changing servers in the app settings. Connecting to a closer server can reduce the time it takes for your data to travel.
Example: If you're in Texas, choose a server in Dallas instead of one in New York or Europe.
6. Check Your VPN
Using a VPN can sometimes increase latency, depending on the server and service.
To test it:
- Turn off your VPN and see if things speed up.
- Or try a different VPN server that’s closer to your real location.
If you rely on a VPN, consider upgrading to one that’s built for low latency.
7. Contact Your Internet Service Provider
If you’ve tried everything and your latency is still high, reach out to your ISP. There could be a problem on their end, like network congestion or outdated infrastructure.
They might:
- Help you switch plans
- Send a technician
- Recommend better equipment
Pro Tip: You can also visit the Broadband Search internet provider tool to compare speeds and service types in your area.
8. Upgrade Your Internet Type
Some types of internet just don’t support low latency. BroadbandSearch explains that some types of internet don’t support low latency. If you're using DSL or satellite and struggling with lag, switching to fiber or cable, as recommended by BroadbandSearch, can make a huge difference. Here are the best uses for common internet types:
- Fiber: 🟢 Excellent - Gaming, video calls, streaming
- Cable: 🟡 Good - Most home use
- DSL: 🔴 Poor - Basic browsing only
- Satellite: 🔴 Very Poor - Not good for real-time use
Visit Broadband Search to compare local providers and see what’s available in your area.
Final Thoughts: Don’t Let Latency Slow You Down
Latency is the hidden cause of many internet headaches—slow websites, glitchy calls, and laggy games. While it’s impossible to get latency down to zero, you can keep it low with a few smart steps. Run a virus scan, restart your router, use a wired connection, and choose the right type of internet (like fiber) for the best performance.
Key Takeaways
- Latency = delay between when you send a request online and get a response.
- Jitter = inconsistency in those response times, making real-time activities worse.
- Fiber internet has the lowest latency, while satellite has the highest.
- Most latency issues can be fixed with restarts, wired connections, and reducing interference.
- Scan your computer for malware to rule out hidden causes.
Need Help Finding a Faster Connection?
If you're ready for smoother browsing, fewer dropped calls, and lag-free gaming, BroadbandSearch can help. Put your internet speed to the test and use our internet provider finder tool to check which low-latency options are available in your area. Just enter your ZIP code to get started!
FAQ
What type of internet connection has the highest latency?
Satellite internet will nearly always have the most latency, often reaching hundreds of milliseconds. It takes a relatively long time for a signal to go into space, get routed through a satellite, and get a response (and then the same in reverse). This is why satellite internet is a very poor choice for online gaming and video calls. However, Starlink, which uses a different satellite network, has much lower latency, if not perfect.
Does more RAM on PC improve internet latency?
No. RAM has nothing to do with your internet service. More RAM can make your programs and applications run more responsively, however. It can make your system feel faster. This might cause people to think that their internet is running better or that they have less latency on their connection.
Does 5G reduce latency?
It depends on what you’re comparing it to. 5G is more of a set of technologies providing internet service than one might tack on to reduce latency. In general, 5G connections will have less latency than 4G connections and some service types. They will likely not have less latency than a fiber internet or wired internet connection. Many factors go into latency, so it can be hard to say for sure.
Can VPNs cause high latency?
They can, but they do not have to. Some VPNs will cause more latency than others. Premium VPNs are generally better for latency than free ones. Additionally, the server one chooses when online with a VPN can make a huge difference when it comes to latency. If you’re only using a VPN for privacy and security purposes, pick the server closest to you to prevent any additional latency from the distance a signal has to travel.
Is 30ms a good latency for online gaming?
Absolutely! While the lower the latency someone has, the better off someone is when it comes to gaming, it’s hard to beat 30ms. Nearly all gamers should be perfectly happy with that, and there should be no issues with gameplay. In general, we recommend that anyone hoping to game online has no more than 70ms of latency. We consider 50ms or less good.