What causes fluctuating internet speeds, and how can you fix them?
Internet speed fluctuations are often caused by your connection type, router settings, signal interference, bandwidth throttling, or hardware limitations. To fix it, start with a speed test, reposition your router, check for malware, and consider upgrading your internet plan or equipment.
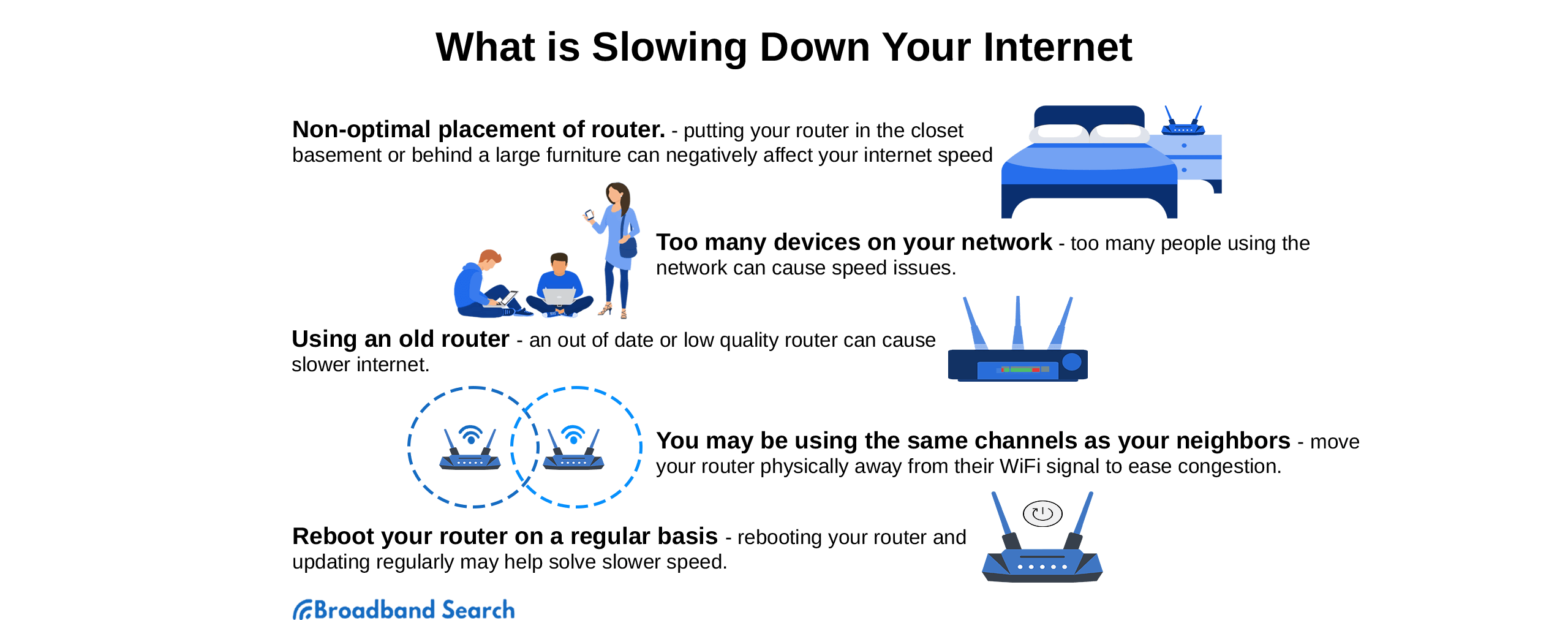
Common Reasons Your Internet Speed Goes Up and Down
1. Your Internet Connection Type Matters
Not all internet connections are created equal. The speed and stability of your connection may depend on the type of service you use:
- DSL / ADSL: Uses copper wires; speed affected by wiring, distance, and congestion
- Cable: Shared bandwidth can slow speeds during peak hours
- Satellite: Affected by weather, high latency, and long-distance signal travel
- Fiber: Fast and stable, but not widely available
- Fixed Wireless: Line-of-sight issues can impact performance
Pro Tip: If fiber is available in your area, it often provides the most consistent speeds.
2. Wi-Fi Signal Strength and Router Placement
Even if your plan is fast, poor Wi-Fi signal can create unstable speeds.
How to Improve Your Wi-Fi Signal:
- Place your router in a central, elevated, and open space.
- Avoid locations near walls, floors, fish tanks, mirrors, and other electronics.
- Do not place your router in the kitchen, as many appliances can block your WiFi — microwave interference is real.
- Point router antennas vertically.
- Use mesh Wi-Fi systems for large or multi-level homes.
Think of Wi-Fi like a sprinkler: the closer your device is, the stronger the signal.
3. Your Router Might Be Holding You Back
Old or misconfigured routers can throttle your speed without you realizing it.
Check These Router Factors:
- Age: Older routers may not support modern internet speeds.
- Bandwidth Limit: Your plan might be 100 Mbps, but your router only supports 50 Mbps.
- Channel Congestion: Use a less crowded Wi-Fi channel to reduce interference from neighbors.
- Wi-Fi Band: Try switching from 2.4 GHz (wider range) to 5 GHz (faster, more stable in close range).
4. Are You Being Throttled by Your ISP?
Some ISPs enforce data caps or throttle users who consume a lot of bandwidth.
Signs of Bandwidth Throttling:
- Internet slows down at the same time each day (especially evenings or weekends)
- Your contract mentions “data limits” or “traffic management”
- Streaming quality drops unexpectedly while other apps work fine
Contact your ISP or check your data usage in your account dashboard. Some plans allow upgrades to remove throttling.
5. Hidden Malware Could Be Slowing You Down
Malware and background processes can steal bandwidth or damage device performance.
Watch for these warning signs:
- Device is hot or fans run constantly
- Slow internet even when no apps are open
- Sudden restarts or crashes
Use antivirus software or malware removal tools to scan and clean your system. Also, update your router’s firmware and change default passwords to protect against external attacks.
6. It Might Not Be You – Server Issues or ISP Limitations
Sometimes your internet slowdown has nothing to do with your home setup. Speed fluctuations can also come from the other end of the line.
If a website’s server is overloaded, like during a major ticket release or product drop, even the best connection won’t help. You might experience slow loading, buffering, or total crashes—but it’s the site, not your Wi-Fi.
Likewise, your ISP’s infrastructure could be the problem. If your neighborhood’s network is outdated or overcrowded, you may notice consistent slowdowns during peak hours—even if you're paying for high-speed internet. In these cases, the issue is often due to limited capacity, not your equipment.
If your internet always slows down at the same time every day, it’s a good sign your ISP’s network is congested.
How to Fix Fluctuating Internet Speeds
There’s no one-size-fits-all fix, but the good news is you can usually do something about it. Whether the issue is inside your home or with your ISP, here are several actions you can take—starting with the simplest and building up from there.
1. Run a Speed Test
Start with a baseline. Use a free tool like TestMySpeed.com to see what speeds you’re actually getting.
- Pro Tip: Run the test multiple times, at different times of day, and on both wired and wireless devices.
- This can help you spot patterns or confirm if you're dealing with a peak-hour slowdown or a Wi-Fi-specific issue.
2. Move Your Modem or Router
Your router’s position affects your entire Wi-Fi network.
- Avoid dead zones by placing your router in a central, elevated, and open area.
- Avoid interference by keeping it away from kitchens, thick walls, mirrors, or large electronics.
- If your house is large or multi-level, consider a mesh Wi-Fi system for stronger whole-home coverage.
3. Update Your Router’s Firmware
Just like phones or laptops, routers need software updates too.
- Log in to your router’s admin panel (check the label on the bottom or side).
- Check for firmware updates and install the latest version.
- Updates often fix bugs, improve speed handling, and patch security flaws.
4. Adjust Frequency Bands and Channels
Modern routers offer both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands:
- 2.4 GHz: Better range, but more interference.
- 5 GHz: Faster, more stable over shorter distances.
You can also manually switch your router’s channel to one with less congestion. This is especially helpful in apartments or neighborhoods with lots of competing networks.
5. Secure Your Network
Make sure your network isn’t being drained by freeloaders or compromised by malware:
- Use WPA2 or WPA3 encryption
- Change the default admin username and password
- Consider using a separate modem and router instead of a combined device from your ISP
6. Monitor When the Issue Happens
Keep a log:
- What time of day does your internet slow down?
- Are you streaming, gaming, or attending a Zoom meeting?
- Are multiple devices using the internet at once?
Tracking patterns can help narrow down whether it's a bandwidth, hardware, or ISP issue.
7. Contact Your ISP
If you’ve tried everything and speeds still fluctuate:
- Call your ISP’s support line and share your speed test results
- Ask if you’re being throttled or if your plan is outdated
- Check if fiber, cable upgrades, or newer hardware options are available
Sometimes, switching providers or upgrading to a higher-tier plan is the only long-term solution.
Final Thoughts: You Can Fix This
Internet isn’t supposed to go fast… then slow… then fast again. Fluctuations usually indicate something is wrong, but with a little troubleshooting, most issues can be resolved at home.
Still stuck? It might be time to upgrade your router, switch plans, or look into faster ISPs available in your area.
Emerging Technologies That Improve Internet Speed Stability
The internet is at the center of how we work, play, and connect with the world—but its reliability can sometimes frustrate us. Fortunately, emerging technologies are here to improve speed and stability, ensuring smoother online experiences. Here’s a closer look at how these innovations are reshaping connectivity.
Wi-Fi 6 and Wi-Fi 6E
- Improved Device Density: Supports more devices simultaneously with less interference than older Wi-Fi versions.
- Better Speed Consistency: Deliverslower latency even in crowded environments like apartments and offices.
- New Frequency Bands: Wi-Fi 6E utilizes the 6 GHz band, which reduces congestion and boosting stable connections.
Mesh Wi-Fi Networks
- Seamless Coverage: Mesh systems use multiple nodes to deliver strong, consistent Wi-Fi throughout your home.
- Eliminate Dead Zones: Stay connected in areas where traditional routers fall short, no matter the size of your space.
5G and 5G Home Internet
- Faster Wireless Speeds: Provides lightning-fast, low-latency internet in urban and suburban areas.
- Alternative to Wired Broadband: A game-changing option for areas with limited access to fiber or cable connections.
Adaptive Bandwidth Management
- Intelligent Traffic Prioritization: Routers dynamically allocate bandwidth to prioritize key tasks like streaming and gaming get top priority.
- Smooth Performance: Helps maintain stable connections during heavy usage, even with multiple devices online.
AI-Powered Network Optimization
- Proactive Problem Solving: AI monitors congestion or interference in real time and resolves issues automatically.
- Peak Performance: Adjusts channel settings and power levels for uninterrupted, high-quality connections.
FAQ
Why does my internet get slow at night?
This is often due to network congestion—more users online during peak hours can strain bandwidth.
Is it better to use Ethernet instead of Wi-Fi?
Yes. A wired connection is faster, more secure, and more stable than Wi-Fi.
Can outdated hardware cause internet problems?
Absolutely. Modems, routers, and even cables should support your plan's maximum speed.
Does fiber internet fluctuate?
Fiber is typically the most stable type of internet, with fewer fluctuations than DSL or cable.
What is considered slow internet?
As mentioned, the FCC considers 25 Mbps download speed, and 3 Mbps upload speed as the minimum standards to qualify as high-speed internet. Taking that into account, we’d say anything less would count as slow.