We're here to provide clear, step-by-step instructions to resolve frustrating Wi-Fi issues and ensure every corner of your home enjoys a robust, reliable connection. Say goodbye to dead zones and sluggish speeds – we have practical solutions tailored to your needs. Significant enhancements are within your grasp.
Assessing Your Current Setup
Assessing your current Wi-Fi setup is the essential first step toward improving your wireless network. This involves two critical aspects: Wi-Fi signal analysis and router assessment.
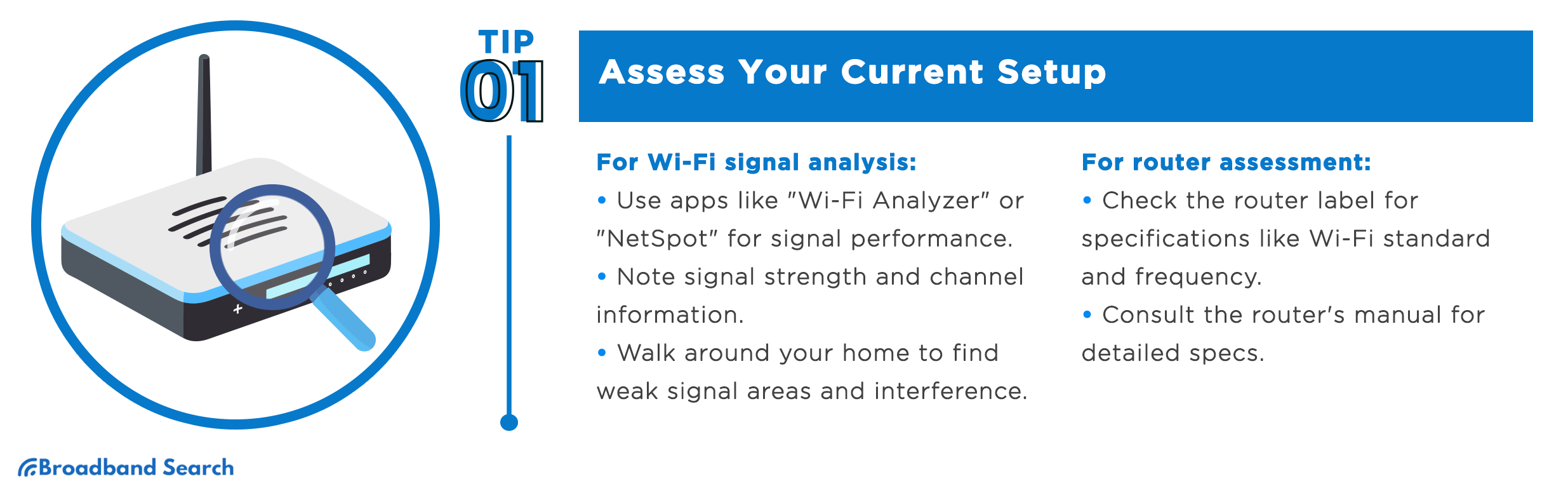
Wi-Fi Signal Analysis
To analyze your Wi-Fi signals effectively:
- Start by downloading a Wi-Fi signal analysis app like "Wi-Fi Analyzer" (for Android) or "NetSpot" (for Windows and macOS). These tools provide visual representations of your Wi-Fi network's performance.
- Open the app and grant the necessary permissions for location access to enable signal analysis.
- In the app, you will typically see a graphical representation of nearby Wi-Fi networks, including yours.
- Focus on the signal strength (measured in dBm or bars) and channel information for your network.
- Walk around your home, visiting each room, and note down the signal strength and potential dead zones. Look for areas with weak signals or interference.
- Pay attention to the channels your network and neighboring networks are using. Identify overcrowded channels that might cause interference.
Performing a Wi-Fi Signal Analysis in Every Room:
- Start in a central location within your home, close to your router.
- Use the Wi-Fi signal analysis app on your smartphone or tablet and take a signal strength measurement.
- Move to different rooms, one at a time, and repeat the signal strength measurement in each room.
- Make note of the signal strength variations and any dead zones where the signal is weak or nonexistent.
- Pay attention to areas with significant signal interference, as this can affect connectivity quality.
Router Assessment
To evaluate your router effectively, it's crucial to understand its specifications. These specifications are usually found on a label on the router itself or in the router's manual.
- Check the Router Label: Locate your router and find the label that displays key specifications. This label often includes the router's model number, Wi-Fi standard (e.g., 802.11ac), frequency (2.4 GHz, 5 GHz), and maximum data transfer rates (e.g., 300 Mbps, 1200 Mbps).
- Consult the Manual: If the label doesn't provide all the necessary information, consult the router's manual. To better understand the router's specifications, familiarize yourself with common terms and functionalities. You can usually find these online by searching for your router's model number on the manufacturer's website.
Identifying the Router's Current Limitations and Signal Range:
Once you understand your router's specifications, it's time to assess its current limitations and signal range:
- Check for Firmware Updates: Visit the router manufacturer's website to see if there are any firmware updates available for your router. Keeping your router's firmware up-to-date can improve its performance and security.
- Assess Signal Range: Walk around your home, noting where the Wi-Fi signal strength begins to drop off. This will help you identify areas with weaker coverage and potential dead zones.
- Observe Interference: Pay attention to potential sources of interference such as neighboring Wi-Fi networks, cordless phones, microwave ovens, and electronic devices. Identifying these sources will be essential for optimizing your Wi-Fi network.
How Can I Extend My Wi-Fi Range?
Once you've assessed your current Wi-Fi setup, the next step is to extend your Wi-Fi range using two effective methods: Using Wi-Fi Range Extenders or Repeaters and the alternative option of Powerline Adapters.

Using Wi-Fi Range Extenders or Repeaters
Extenders or repeaters are devices designed to boost your Wi-Fi signal. To optimize their effectiveness, follow these placement guidelines:
- Find the Right Location: Identify the areas with weak Wi-Fi coverage or dead zones in your home. These are the places where you should consider placing your Wi-Fi extender.
- Midpoint Positioning: Position the extender between your router and the area with poor coverage. This ensures it can effectively capture and amplify the existing signal.
- Avoid Obstacles: Keep the extender away from walls, large furniture, or other obstructions. A clear line of sight between the extender and your router is ideal.
- Test and Adjust: After initial placement, use your Wi-Fi signal analysis tool to check the signal strength in the extended area. Adjust the extender's position as needed to achieve the best results.
To configure your Wi-Fi extender, follow these general steps (specific instructions may vary depending on the extender model):
- Connect to the Extender: Use a computer or smartphone to connect to the extender's Wi-Fi network. This network name is often similar to your router's network with "_EXT" or "_EXTENDER" appended to it
- Access the Extender's Settings: Open a web browser and enter the IP address provided in the extender's manual (e.g., 192.168.0.1). Log in using the default credentials or those provided in the manual.
- Select Your Network: Locate the list of available Wi-Fi networks and choose your existing Wi-Fi network. Enter the password when prompted.
- Configure Settings: Follow the on-screen instructions to configure your extender. You can usually leave most settings as default, but verify that the SSID (network name) and password match your existing network.
- Save and Reconnect: Once configured, save the settings and allow the extender to restart. Reconnect your devices to the extended Wi-Fi network.
- Signal Check: Use your Wi-Fi signal analysis tool to check the signal strength in the previously weak area. If needed, adjust the extender's position for optimal coverage.
Alternative: Powerline Adapters
Powerline adapters use your home's electrical wiring to transmit data signals. Here's how they work:
- Pairing Adapters: You'll typically get two powerline adapters in a kit. Connect one to your router using an Ethernet cable, and plug it into a nearby power outlet. Then, take the second adapter and plug it into a power outlet in the room where you need better Wi-Fi coverage.
- Data Transmission: The first adapter sends your internet data signals into the electrical wiring of your home. The second adapter receives these signals and broadcasts them as a Wi-Fi network, effectively extending your network to that room.
Step-by-step instructions for setting up powerline adapters:
- Unpack and Plug In: Unbox the powerline adapter kit and plug one adapter into an electrical outlet near your router. Connect it to your router using an Ethernet cable.
- Place the Second Adapter: Take the second adapter and plug it into an electrical outlet in the room where you want improved Wi-Fi coverage.
- Pair the Adapters: Most powerline adapters have a "pair" or "sync" button. Press this button on both adapters within a short time frame (usually a minute) to pair them. They'll create a secure connection.
- Configure Wi-Fi (if applicable): Some powerline adapters have built-in Wi-Fi. Access the adapter's settings through a web browser (use the IP address provided in the manual) to set up the Wi-Fi network's name (SSID) and password.
- Connect Devices: Once configured, connect your devices to the newly extended Wi-Fi network. Use your Wi-Fi signal analysis tool to check the signal strength and make any adjustments if needed.
Pros and Cons: Powerline Adapters vs. Wi-Fi Range Extenders
Powerline Adapters:
Pros:
- Reliable Connection: Powerline adapters create a stable wired connection through your home's electrical wiring, often resulting in more consistent speeds than Wi-Fi.
- Easy Setup: Simply plug the adapters into electrical outlets, pair them, and you're ready to go.
- Multiple Ethernet Ports: Many powerline adapter kits offer multiple Ethernet ports on the receiving end, allowing you to connect several wired devices.
Cons:
- Dependent on Electrical Wiring: The effectiveness of powerline adapters can vary depending on the quality and age of your home's electrical wiring.
- Limited Wi-Fi Coverage: While some models have built-in Wi-Fi, they may not cover as large an area as dedicated Wi-Fi range extenders.
- Cost: Quality powerline adapter kits can be relatively more expensive compared to some Wi-Fi range extenders.
Wi-Fi Range Extenders:
Pros:
- Extended Wi-Fi Coverage: Range extenders are designed specifically for Wi-Fi coverage extension, making them suitable for larger areas.
- Universal Compatibility: They work with all Wi-Fi-enabled devices, regardless of the device's ports or connectivity options.
- Affordable Options: There are budget-friendly range extenders available that provide a good balance between cost and performance.
Cons:
- Speed Variability: Extenders may introduce some speed loss due to the additional wireless hop, especially if the signal has to go through multiple walls.
- Complex Setup: Setting up Wi-Fi extenders may involve more configuration steps compared to powerline adapters.
- Signal Interference: Depending on the placement and configuration, extenders may suffer from signal interference or create overlapping Wi-Fi networks, which can be confusing for users.
What Is Mesh Wi-Fi?
Mesh Wi-Fi is a network system that uses multiple interconnected nodes to provide seamless internet coverage throughout your entire home. This section will delve into the core concepts of Mesh Wi-Fi technology and guide you through setting up a Mesh Wi-Fi system for your home.

In-Depth Explanation of Mesh Wi-Fi
Mesh Wi-Fi systems work by creating a network of interconnected nodes, with one node acting as the primary router connected to your modem. Here's how it functions:
- Nodes: A mesh Wi-Fi system consists of multiple nodes. One of them is connected to your modem and serves as the main router, while the others are satellite nodes.
- Smart Routing: The nodes communicate with each other to form a unified network. They intelligently determine the best path for data transmission, optimizing signal strength and minimizing interference.
- Self-Healing: If one node fails or experiences interference, the mesh network automatically reroutes data through other nodes. This self-healing capability ensures continuous connectivity even if a node encounters issues.
- Seamless Roaming: Mesh systems support seamless roaming, allowing your devices to connect to the node with the strongest signal as you move throughout your home. This eliminates dropped connections and slow handoffs.
Benefits of Mesh Systems over Traditional Setups
Mesh Wi-Fi systems offer several advantages over traditional router and range extender setups:
- Whole-Home Coverage: Mesh systems provide uniform coverage throughout your entire home, including areas that are typically Wi-Fi dead zones.
- Easy Expansion: You can expand your mesh network by adding more nodes, ensuring consistent coverage as your needs grow.
- Simplified Management: Most mesh systems come with user-friendly apps that make setup and management a breeze, even for non-technical users.
- Seamless Roaming: With mesh, your devices seamlessly switch between nodes without interruption, enhancing your experience with mobile devices and streaming.
How Do I Set Up Mesh Wi-Fi?
To set up Mesh Wi-Fi, you need to first find the best placement for the nodes. Proper node placement is crucial for maximizing the effectiveness of your mesh Wi-Fi system:
- Initial Node Placement: Start by connecting the primary node (usually labeled as the main router) to your modem. Place it in a central location within your home to provide an even Wi-Fi footprint.
- Satellite Nodes: Position satellite nodes in areas with weak or no Wi-Fi signal. Nodes should be placed within a reasonable line of sight of each other for optimal performance.
- Avoid Obstacles: Keep nodes away from physical obstructions like walls, large furniture, or electronic devices that could interfere with the signal.
- Test Signal Strength: Use your Wi-Fi signal analysis tool to check signal strength in different areas and adjust node placement as needed.
Step-by-Step Configuration Using the Manufacturer's App:
Configuring your mesh Wi-Fi system is typically straightforward, thanks to manufacturer-provided apps.
- Download the App: Download the manufacturer's app from your device's app store.
- Connect to the Main Node: Open the app and follow the on-screen instructions to connect to the main node, usually via Bluetooth or a QR code.
- Node Detection: The app will detect satellite nodes and guide you through the process of adding them to your network.
- Network Configuration: Customize your network name (SSID) and password, if desired, and set other preferences like parental controls.
- Placement Guidance: Many apps provide placement recommendations to optimize your network. Follow these suggestions for node placement if offered.
- Finalization: Complete the setup process and allow the system to configure itself. The nodes will communicate and self-optimize for the best signal distribution.
How Can I Improve My Wi-Fi?
Fortunately, there are several steps you can take to improve your Wi-Fi speed and performance. Let's start with Channel Optimization.

Channel Optimization
Wi-Fi operates on different channels within the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands. To optimize your Wi-Fi speed and reduce interference, follow these steps:
- Access Your Router's Settings: Log in to your router's web interface using a web browser. Refer to your router's manual or search online for instructions on how to access these settings.
- Find the Wi-Fi Channel Settings: Look for the wireless settings section in your router's interface. You'll find options related to channels there.
- Check Current Channel Usage: Most routers will display a list of available Wi-Fi channels and their current usage. Identify which channels are less congested, typically those with fewer neighboring networks on the same channel.
- Change to a Less Congested Channel: Once you've identified a less congested channel, switch your router to that channel. Save the settings, and your router will restart with the new channel.
- Monitor and Adjust: Keep an eye on your Wi-Fi performance over time. If you notice interference or a decline in speed, you may need to repeat the process and choose a different channel.
Explaining Advanced Techniques like DFS Channel Usage:
Dynamic Frequency Selection (DFS) channels offer advanced options for optimizing your Wi-Fi network. These channels are less crowded because they are shared with radar systems. Routers equipped with DFS capabilities can automatically switch to these channels when radar activity is low, providing a less congested and potentially faster Wi-Fi experience.
To take advantage of DFS channels, it's important to ensure your router supports them. Check your router's specifications or settings to see if DFS channels are available. If your router supports DFS, enable this feature in your router settings to unlock the benefits of these less crowded channels.
While DFS channels can offer better performance, it's essential to be aware that they may require periodic channel changes to avoid radar interference. Fortunately, modern routers equipped with DFS are designed to handle these channel adjustments automatically, ensuring a reliable and optimized Wi-Fi connection.
Enhancing Range with Wi-Fi Boosters and Antennas
High-gain antennas can extend your Wi-Fi range and improve signal strength. Here's how to choose and install them:
- Determine Compatibility: Check your router's compatibility with external antennas. Many routers have detachable antennas. If yours does, you can typically replace them with high-gain antennas.
- Choose the Right Antenna Type: Select high-gain antennas that match your router's frequency (2.4 GHz or 5 GHz). Also, consider the antenna's gain rating, typically measured in dBi. Higher gain antennas provide better range but may be directional.
- Installation: To install high-gain antennas, unscrew the existing antennas from your router and screw in the new ones. Position the antennas vertically for omnidirectional coverage or adjust them according to your needs.
Usage of Wi-Fi Boosters Specifically Designed for Individual Devices and Setup:
Wi-Fi boosters designed for individual devices, such as Wi-Fi range extenders or USB adapters, can improve signal strength for specific devices. To set them up you have to:
- Select a Wi-Fi booster that suits your needs. USB adapters are suitable for laptops, while plug-in extenders work well for smartphones, tablets, and other devices.
- For plug-in extenders, simply plug them into an electrical outlet within range of your router. Follow the manufacturer's setup instructions, typically using a smartphone app or web interface.
- To install a USB adapter, plug it into an available USB port on your computer. Install any drivers or software that come with the adapter, and follow on-screen instructions for configuration.
- Connect your device to the newly created Wi-Fi network provided by the booster. Enter the network's password if prompted.
Wi-Fi 6/6E: The Smart Upgrade for Your Home Network
Say Goodbye to Bottlenecks
Wi-Fi 6/6E is built to handle the demands of modern homes, managing dozens of devices simultaneously without breaking a sweat. Its advanced Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access (OFDMA) technology splits channels to reduce congestion and keep your smart home, streaming, and remote work running smoothly.
Faster, Smarter, Stronger
With speeds up to 9.6 Gbps and access to the 6 GHz band (Wi-Fi 6E), you’ll enjoy faster, more stable connections — perfect for 4K/8K streaming, gaming, and video calls. Lower latency and higher bandwidth mean no more buffering or lag, even during peak usage.
Reliable Coverage Where You Need It
Wi-Fi 6/6E is designed for dense living spaces like apartments or offices, cutting through interference for consistent performance. Features like Target Wake Time (TWT) also optimize device battery life, making your entire network more efficient.
Future-Proof Your Network
Don’t just upgrade — invest in a solution that lasts. With more devices supporting Wi-Fi 6 and Wi-Fi 6E adoption growing rapidly, upgrading now ensures your network stays ahead of the curve for years to come. It’s not just better Wi-Fi; it’s a smarter, future-ready solution to your biggest connectivity challenges.
Comparing Wi-Fi Extenders, Mesh Systems, and Wi-Fi 6/6E Routers
| Option | Pros | Cons | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wi-Fi Extenders | Low cost, easy to set up | Halves bandwidth, spotty performance | Small apartments, fixing one dead zone |
| Mesh Systems | Whole-home coverage, seamless roaming, scalable | Higher upfront cost | Large or multi-story homes, families with many devices |
| Wi-Fi 6/6E Routers | Faster speeds, lower latency, handles many devices, future-proof | May not fully cover very large homes alone | Medium–large homes, heavy streaming/gaming, smart homes |
How Do I Secure My Wi-Fi?
Securing your Wi-Fi starts with implementing strong security measures to protect your network from unauthorized access and potential cyber threats.
Implementing Robust Encryption (WPA3)
WPA3 encryption provides state-of-the-art security for your Wi-Fi network, ensuring both data protection and optimal performance. Follow these steps to enable it on your router:
- Access Router Settings
- Open a web browser and enter your router's IP address (e.g., 192.168.1.1) into the address bar, then press Enter. Log in using your admin username and password. If you're unsure of these details, check your router's manual or the label on your device.
- Navigate to Wireless Settings
- After logging in, locate the wireless settings or security section. This might appear as "Wireless Security," "Wi-Fi Settings," or similar.
- Enable WPA3 Security
- Within the wireless security options, find the encryption type setting. Choose "WPA3" or "WPA3-Personal" if available. For older devices, you may need to use "WPA2/WPA3" for compatibility.
- Set a Strong Wi-Fi Password
- Create a unique, difficult-to-guess password for your network. Use a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols. Avoid easily guessable passwords like "12345678" or personal names.
- Save and Reboot
- Save your changes. Your router might prompt you to reboot to apply the settings. Confirm the reboot and wait for your router to restart.
- Reconnect Devices
- After completing the setup, reconnect all your Wi-Fi devices to the network using the updated password.
Why Strong Encryption Matters
- Data Privacy
- Encryption ensures all data transmitted over your Wi-Fi network stays private and secure, protecting sensitive information such as passwords and financial details.
- Defense Against Cyber Threats
- Robust encryption makes it significantly harder for attackers to intercept and decode your data, safeguarding you from eavesdropping and man-in-the-middle attacks.
- IoT Device Protection
- With smart home devices increasingly part of daily life, strong encryption helps secure these often vulnerable endpoints from potential hacks.
- Compliance and Responsibility
- Using strong encryption fulfills an ethical and sometimes legal obligation to protect personal data and privacy.
By enabling robust encryption and setting up a secure Wi-Fi network, you'll create a safer online environment for yourself and all connected devices in your home.
How to Troubleshoot Common Wi-Fi Issues
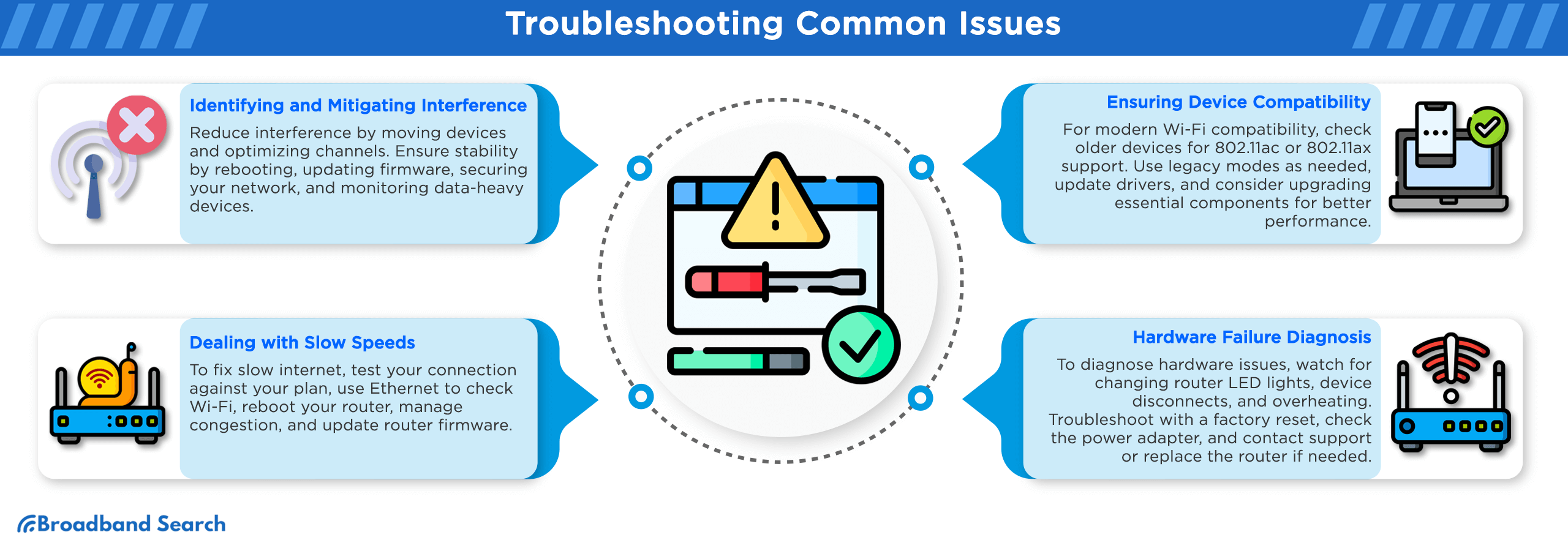
Identifying and Mitigating Interference
Interference from other electronics is a frequent cause of Wi-Fi issues. Here's how to minimize it:
- Identify Sources of Interference: Check for devices near your router, like cordless phones, microwaves, or baby monitors, which may interfere with the signal.
- Relocate Your Router: Place your router away from these devices and other physical obstructions. Elevating it to a higher position can also enhance signal quality.
- Switch Wi-Fi Channels: Use your router's settings to select less congested channels, particularly in the 2.4 GHz band.
- Use the 5 GHz Band: If supported, switch to the 5 GHz band for a less crowded, interference-resistant connection.
Improving Wi-Fi Stability
Stable connectivity is essential for smooth online activities. Try these strategies to enhance your Wi-Fi network's stability:
- Restart Your Router: A simple reboot often resolves minor problems.
- Update Firmware: Check that your router's firmware is up-to-date to ensure optimal performance and security.
- Reposition Your Router: Adjust your router’s location to maximize coverage. Consider adding extenders for larger spaces.
- Secure Your Network: Use a strong password to protect your Wi-Fi and prevent unauthorized access, which can cause interference.
- Monitor Traffic: Identify and manage bandwidth-heavy devices or applications using network monitoring tools.
Addressing Slow Speeds
Slow internet speeds can disrupt your activities. Follow these steps to troubleshoot and resolve speed-related problems:
- Run a Speed Test: Use a speed testing tool to compare your current speed to your internet plan.
- Test Ethernet Connectivity: Connect a device directly to the router with an Ethernet cable to determine if the issue is with Wi-Fi or the internet connection.
- Reboot Your Router: Clear potential temporary issues with a router restart and check for improvements.
- Reduce Network Congestion: Check if multiple devices are overloading the network. Prioritize tasks or consider upgrading your internet plan if needed.
- Update Firmware: Outdated firmware can impact speed, so ensure your router is running the latest version.
Ensuring Device Compatibility
Older devices may not function well with the latest Wi-Fi standards, but there are solutions to maintain connectivity:
- Check Compatibility: Verify that your devices support Wi-Fi standards like 802.11ac or 802.11ax in their specifications.
- Use Legacy Modes: If supported, switch older devices to the 2.4 GHz band for compatibility—though speeds may be slower.
- Update Drivers: Regularly update device drivers to improve their performance with newer Wi-Fi technologies.
- Prioritize Upgrades: Consider upgrading key devices, like your router, to enhance overall network performance. Trade-in programs or budget-friendly options can help lower costs.
Diagnosing Hardware Failure
Occasionally, Wi-Fi disruptions may stem from hardware issues. Watch for these signs and take action when needed:
- Check Router LEDs: Sudden changes or inactive status lights could indicate a hardware problem.
- Monitor Device Behavior: Repeated disconnections may signal router issues.
- Prevent Overheating: Ensure the router is ventilated and not exposed to extreme temperatures.
Steps to Resolve Hardware Issues
- Factory Reset: Restore your router to its default settings if issues persist. Check the manual for instructions.
- Verify Power Supply: Ensure the power adapter is functioning properly with the correct voltage.
- Seek Support: If problems remain unresolved, contact the manufacturer or replace the router.
By following these steps, you can troubleshoot and resolve most common Wi-Fi issues, ensuring a stable and secure connection for your devices.
Future-Proofing Your Setup
Future-proofing your Wi-Fi setup is crucial to ensure that your network remains relevant and capable of handling emerging technologies.
Staying Informed about Emerging Technologies
Staying informed about emerging Wi-Fi technologies is vital to future-proofing your setup. Make it a habit to regularly check these sources, participate in discussions, and engage with the Wi-Fi community. Being proactive in learning about upcoming advancements will empower you to make informed decisions when upgrading your network.
Sources and Platforms to Keep Updated on the Latest Wi-Fi Trends:
- Tech News Websites: Regularly visit tech news websites like CNET, TechCrunch, Ars Technica, and The Verge for articles and updates on emerging Wi-Fi technologies.
- Official Wi-Fi Alliance Website: The Wi-Fi Alliance's official website (wi-fi.org) provides information on new Wi-Fi standards, certifications, and advancements.
- Forums and Communities: Join online forums like Reddit's r/WiFi and tech communities on platforms like Stack Exchange and Tom's Hardware to discuss and learn about the latest Wi-Fi developments.
- Manufacturer Blogs: Follow blogs and news sections on router manufacturer websites (e.g., ASUS, TP-Link, Netgear) for announcements about new products and technologies.
- Social Media: Follow Wi-Fi experts and tech enthusiasts on Twitter, LinkedIn, or other social media platforms for real-time updates and discussions.
Planning for Future Upgrades
Comprehensive Guide on Creating a Roadmap for Future Wi-Fi Enhancements:
- Assess Current Needs: Begin by evaluating your current and anticipated Wi-Fi requirements. Consider the number of devices, types of activities (e.g., streaming, gaming, smart home), and the size of your home.
- Research Emerging Technologies: Stay informed about emerging Wi-Fi standards, such as Wi-Fi 7 and beyond. Understand their capabilities and how they can benefit your network.
- Budget Planning: Set aside a budget for future Wi-Fi upgrades. Consider both the cost of new equipment and any potential installation or professional setup fees.
- Device Compatibility: Ensure that your existing and planned devices are compatible with the latest Wi-Fi standards. Some older devices may require upgrades or replacements.
- Mesh Networking: Explore the possibility of upgrading to a mesh Wi-Fi system if you haven't already. Mesh systems offer scalability and adaptability to changing network needs.
- Smart Home Integration: Plan for the integration of smart home devices and IoT into your network. Consider a separate network for IoT devices to enhance security.
- Security Measures: Stay vigilant about network security by keeping router firmware up-to-date and using strong encryption. Consider investing in security solutions like VPNs or security-focused routers.
- Professional Consultation: If your network needs are complex or you're unsure about future upgrades, consult with a networking professional who can provide tailored advice.
Next Steps for Stronger Wi-Fi
- A strong Wi-Fi connection is essential today. Ready to boost your signal and enjoy a seamless online experience? Here are your next steps:
- First, assess your current setup. For small weak spots, a simple extender can help. For whole-home coverage in larger spaces, a mesh Wi-Fi system is ideal. For top speeds and future-proofing, consider a Wi-Fi 6 or 6E router.
- Router placement is key. Moving it to a central, open spot, away from obstructions, can significantly boost performance. Also, keep your router's firmware updated for better security and speed.
- To fine-tune your network, use a free Wi-Fi analyzer app (like Fing). These tools help pinpoint weak zones, check interference, and confirm improvements. Test and adjust as needed.
- Thinking ahead, investing in newer hardware can save future headaches. With Wi-Fi 7 on the horizon, staying aware of new developments ensures your network remains cutting-edge.
Ready for a stronger network? Whether it’s moving your router, updating software, or exploring new gear, a more reliable home connection is within your reach.
FAQ
What is the best frequency band for Wi-Fi, 2.4 GHz, or 5 GHz?
The choice between 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz depends on your specific needs. 2.4 GHz offers a better range and can penetrate walls easily, making it suitable for larger homes. On the other hand, 5 GHz provides faster speeds but has a shorter range, making it ideal for high-bandwidth activities like gaming and streaming. Dual-band routers that support both frequencies offer flexibility.
How can I eliminate Wi-Fi dead zones in my home?
Dead zones can be eliminated by using Wi-Fi range extenders, powerline adapters, or mesh Wi-Fi systems. These devices help extend the reach of your Wi-Fi signal to cover areas that were previously lacking in coverage.
What can I do to improve my Wi-Fi speed and performance?
You can optimize your Wi-Fi speed and performance by ensuring your router's firmware is up to date, choosing the least congested Wi-Fi channels, using high-gain antennas, and considering boosters or repeaters if needed. Additionally, close background apps and limit concurrent connections for improved speed.
How can I make older devices compatible with newer Wi-Fi technologies?
To make older devices compatible with newer Wi-Fi technologies, you can change your router's wireless mode to one that older devices support (e.g., 802.11n). Alternatively, you can use external Wi-Fi adapters or upgrade the devices themselves if possible.
Is upgrading to Wi-Fi 6E or Wi-Fi 7 worth it for full-home coverage?
Upgrading to Wi-Fi 6E or Wi-Fi 7 can provide significant benefits depending on your specific needs and setup. Pros include better throughput, reduced congestion, and access to more channels, especially in the 6 GHz band for Wi-Fi 6E or the advancements with Wi-Fi 7. However, keep in mind that upgrading requires compatible devices to leverage these technologies, and the cost of new hardware may be a factor. Before upgrading, check whether your current devices support these standards, evaluate the size of your home, and consider your existing mesh system or antenna setup to determine if the benefits are worth the investment.
How much speed do I lose when using an extender vs. mesh vs. powerline?
The speed loss depends on the technology used and your home’s environment. Wi-Fi extenders often reduce bandwidth by 30-50% because they rely on a wireless hop to extend coverage. Powerline adapters' performance varies based on the quality of your home's electrical wiring and interference from other devices. Mesh systems generally offer better performance, but speeds can depend on node placement and the overall network configuration. Testing each option in your environment may help determine the best fit for your needs.
What’s the best way to place mesh nodes or extenders for optimal coverage?
The best position for mesh nodes or extenders is midway between your router and the areas with poor connectivity. Ensure they have a clear line of sight if possible, and avoid placing them near thick walls, metal objects, or other materials that can obstruct wireless signals. Then, test the signal strength in different areas of your home and adjust the placement as needed to maximize performance.
How do I test for interference and choose the best Wi-Fi channel?
To test for interference, use Wi-Fi analyzer apps that can detect which channels are overcrowded. For 2.4 GHz networks, avoid overlapping channels and stick to channels 1, 6, or 11 for better performance. To reduce interference, switch to 5 GHz when possible, as it offers less congestion. If your router supports Dynamic Frequency Selection (DFS) channels, consider using these for additional options, especially in areas with minimal interference. Monitoring your network can help ensure you are always on the best channel.